Imagine you have a team of highly specialized experts, each brilliant in their own field. One is a master chef, another a meticulous accountant, and a third, a savvy marketing guru. Now, imagine they all speak different languages. How would they collaborate on a grand project, like opening a new restaurant? It would be a chaotic mess!
This is pretty much the problem we face with AI agents today. We have incredible AI models (the “experts”) that can do amazing things, like summarize documents, analyze data, or even write code. But when you want them to work together on a complex task, it’s like trying to get them to speak different languages. Each AI is often built on different platforms, with different rules and ways of communicating, leading to a lot of headaches for developers.
Enter Google’s Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol – the “universal translator” for AI agents.

What is A2A in Simple Terms?
A2A is an open standard (think of it like a common rulebook) that allows different AI agents, regardless of who built them or what technology they use, to talk to each other seamlessly. It gives them a shared language and a clear way to understand each other’s requests, share information, and work together on tasks.
Think of it this way:
- Before A2A: If Agent A (built by Google) needed to work with Agent B (built by another company), developers would have to write a lot of custom code, like building a special bridge, just for those two to communicate. If you added Agent C, you’d need another custom bridge. It gets complicated, fast!
- With A2A: Agents simply follow the A2A rulebook. Now, Agent A can send a message to Agent B, and Agent B understands it perfectly, and vice-versa. No more custom bridges for every pairing! It’s like everyone learning a common tongue, making collaboration much easier and more efficient.
Why is A2A a Big Deal?
- Breaking Down Silos: Many businesses use different AI tools for different tasks. A2A allows these isolated tools to finally work together, creating more powerful and comprehensive AI systems.
- Simplified Collaboration: Instead of writing complex, custom integrations, developers can rely on A2A to handle the communication. This speeds up development and makes it easier to build multi-agent systems.
- Scalability: As you add more AI agents to your system, A2A ensures they can all communicate without the whole system becoming unmanageable. It’s built for large-scale, enterprise-level AI applications.
- Vendor Neutrality: A2A is an open protocol, meaning it’s not tied to any single company or platform. This encourages innovation and allows developers to choose the best AI agents for their needs, regardless of their origin.
- Handling Complex Tasks: Imagine an AI system that helps you plan a trip. Instead of one huge, clunky AI, you could have:
- A “Flight Agent” that finds the best flights.
- A “Hotel Agent” that books accommodation.
- A “Tour Agent” that suggests activities.
- A “Budget Agent” that keeps track of expenses. With A2A, these agents can talk to each other, coordinate, and work together to plan your entire trip seamlessly.
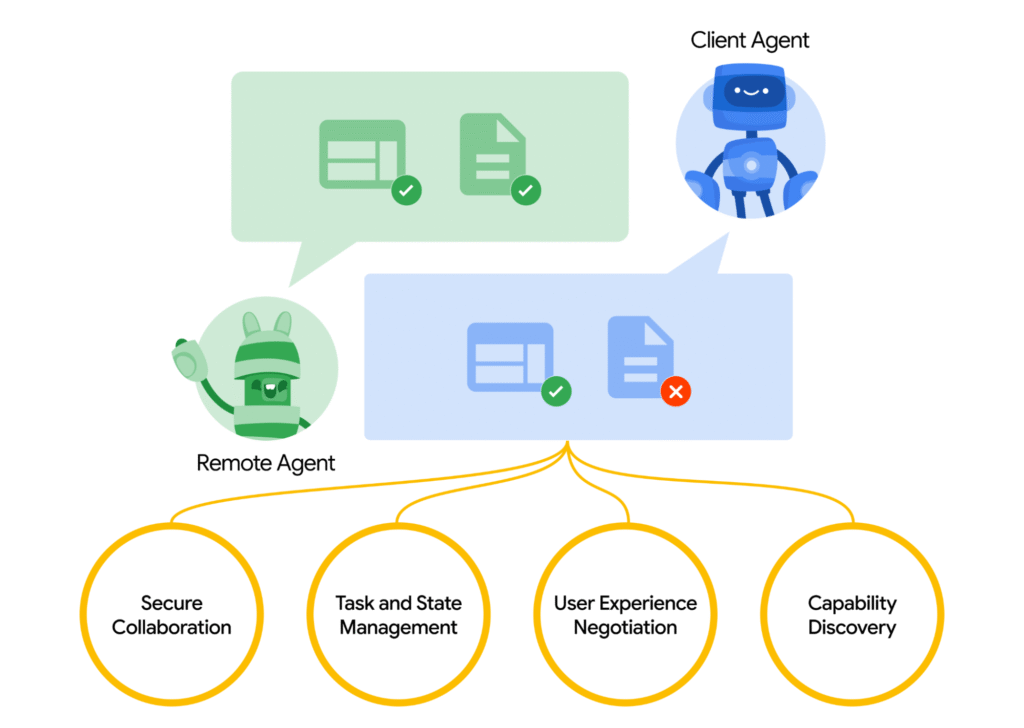
How Does A2A Work (A Little Bit Under the Hood)?
A2A is built on familiar web technologies, which makes it easy for developers to adopt:
- HTTP/HTTPS: The same way your web browser talks to websites, A2A agents use HTTP for sending and receiving messages securely.
- JSON-RPC: This is a standardized way for agents to send structured messages to each other, like giving commands or sharing data.
- Agent Cards: Each AI agent can publish an “Agent Card,” which is like its resume. It describes what the agent can do, what kind of information it needs, and how to communicate with it. Other agents can “discover” these cards to find the right partner for a task.
- Task Management: A2A allows agents to track the progress of complex tasks, sending updates and managing the entire workflow from start to finish. It even handles long-running tasks, where human input might be needed along the way.
- Multimodal Support: It’s not just about text! A2A can handle various types of information, including forms, audio, video, and file attachments, making interactions richer and more human-like.
Real-World Examples of A2A in Action:
- Customer Support: Imagine a customer support bot that can talk to a “Returns Agent,” an “Inventory Agent,” and a “Shipping Agent” to handle a complex customer request, all without a human needing to switch between different systems.
- Financial Services: AI agents could collaborate on fraud detection, with one agent analyzing transaction patterns, another cross-referencing data from different banks, and a third assessing real-time risk.
- Smart Cities: A traffic management AI could communicate with a public transportation routing AI to dynamically adjust routes and reduce congestion in real-time.
- Supply Chain Management: Agents could coordinate inventory, logistics, and delivery across various systems to optimize the entire supply chain.
The Future of AI is Collaborative
Google’s Agent2Agent Protocol is a significant step towards a future where AI agents aren’t just isolated tools, but rather a collaborative digital workforce. By providing a common language and a clear set of rules for communication, A2A is paving the way for more intelligent, interconnected, and powerful AI systems that can tackle increasingly complex challenges. It’s about making AI agents work together as effortlessly as a well-oiled human team.
Read more about A2A Protocol here – https://a2aprotocol.ai/
Also Read About: https://blog.vanijyatech.in/model-context-protocol-mcp-usb-c-for-ai-agents/





Very informative and well written.
Helped me understand the topic better.
Clear explanation with practical insights.
Great article, learned something new.
Useful information for beginners.
Well structured and easy to read.
This answered many of my questions.
Good examples and explanations.
Highly recommended for readers.
Thanks for sharing this valuable content.
Very informative and well written.
Helped me understand the topic better.
Clear explanation with practical insights.
Great article, learned something new.
Useful information for beginners.
Well structured and easy to read.
This answered many of my questions.
Good examples and explanations.
Highly recommended for readers.
Thanks for sharing this valuable content.